Diabetes and heart disease: What is the connection?
What is Heart Disease?
Heart disease encompasses a variety of conditions affecting the heart, including coronary artery disease, heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias), and heart defects present at birth. The most common type, coronary artery disease (CAD), occurs when the blood vessels supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart are narrowed or blocked by fatty deposits, known as plaques. This results in reduced blood flow, which can lead to chest pain (angina), heart attacks, or even heart failure.
Symptoms of Heart Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of heart disease is crucial for early intervention. Common signs include:
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
What is Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin. This leads to elevated levels of glucose in the bloodstream, which can cause serious health complications over time.
Symptoms of Diabetes
The symptoms of Type 2 diabetes often develop gradually and can be subtle. They include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
- Areas of darkened skin, often in the armpits or neck
The Connection Between Diabetes and Heart Disease
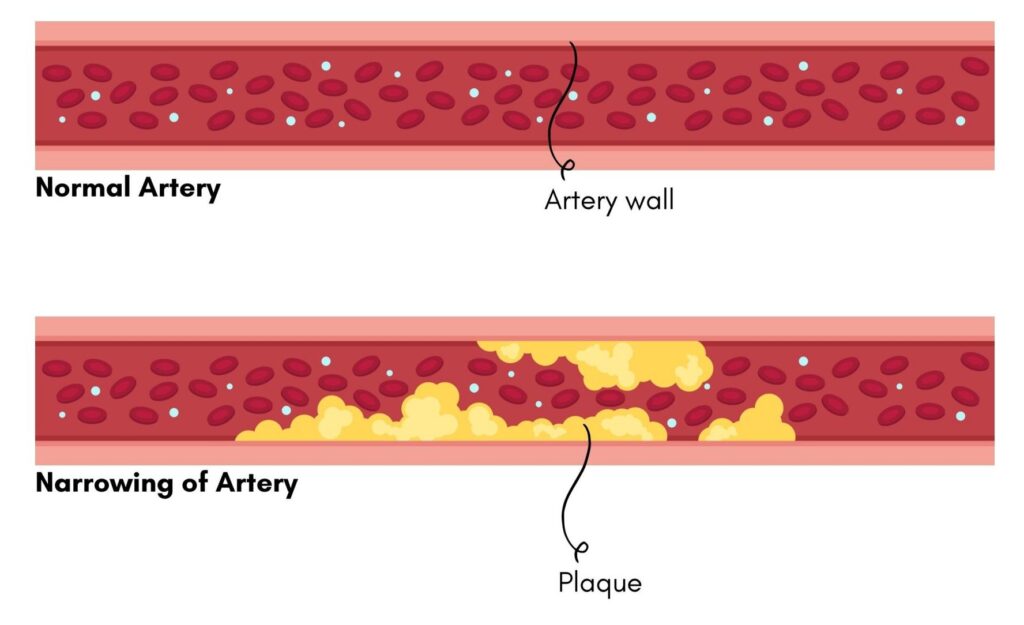
The links between Type 2 diabetes and heart disease are well documented. Research indicates that individuals with diabetes are twice as likely to develop heart disease compared to those without. The relationship can be attributed to several factors:
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance contributes to higher blood sugar levels, which can lead to inflammation and damage to blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- High Blood Pressure: Many individuals with diabetes also have hypertension, a major risk factor for heart disease.
- Dyslipidemia: People with diabetes often have abnormal cholesterol levels, which can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation, often seen in diabetes, can negatively affect heart health.
Understanding this connection emphasizes the importance of effectively managing both conditions to reduce the risk of serious health complications.
Best Diet for Heart Disease and Diabetes
A well-balanced diet is critical for managing both heart disease and Type 2 diabetes. The following dietary strategies can help:
1. Emphasize Whole Foods
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread)
- Lean proteins (skinless poultry, fish, legumes)
- Healthy fats (olive oil, avocados, nuts)
2. Control Portion Sizes
Monitoring portion sizes can help manage blood sugar levels and prevent weight gain, which is beneficial for heart health.
3. Limit Saturated and Trans Fats
Reduce the intake of unhealthy fats found in:
- Processed and fried foods
- Fatty cuts of meat
- Full-fat dairy products
4. Reduce Sodium Intake
High sodium intake can lead to elevated blood pressure. Aim for less than 2,300 mg of sodium per day, and consider even less (1,500 mg) for greater health benefits.

5. Monitor Carbohydrate Intake
Focusing on complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Opt for:
- Whole grains
- Fruits with high fiber content
- Non-starchy vegetables
6. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps to regulate blood sugar levels and supports overall heart health.
Testing for Heart Disease
Regular testing is essential for early detection and management of heart disease, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Key tests include:
1. Blood Pressure Monitoring
Routine blood pressure checks can help identify hypertension early, allowing for timely intervention.
2. Cholesterol Tests
A lipid panel measures levels of LDL (bad) and HDL (good) cholesterol and triglycerides, providing insights into heart disease risk.
3. Blood Glucose Testing
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for managing diabetes and can help prevent complications that affect heart health.
4. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG records the heart’s electrical activity and can help diagnose arrhythmias or other heart issues.
5. Stress Testing
This test evaluates how the heart performs under physical stress and can help identify coronary artery disease.
6. Imaging Tests (e.g., Echocardiogram)
Echocardiograms provide detailed images of the heart’s structure and function, aiding in the diagnosis of various heart conditions.
How to Take Care of the Heart with Diabetes
Individuals with Type 2 diabetes can take proactive steps to care for their heart health. Here are essential strategies:
1. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise can help control weight, reduce blood sugar levels, and lower blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, including:
- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
2. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Keeping blood sugar levels within target ranges is vital for preventing complications that can affect heart health.
3. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively impact both diabetes and heart health. Consider incorporating stress-reducing activities such as:
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Deep breathing exercises
4. Quit Smoking
If you smoke, seek support to quit. Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease and can worsen diabetes complications.
5. Follow a Medication Plan
Taking prescribed medications as directed and attending regular healthcare appointments can help manage both conditions effectively.
6. Stay Informed
Educating yourself about both diabetes and heart disease will empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Engage with healthcare professionals who can help guide your care.
Conclusion

The intertwining of Type 2 diabetes and heart disease necessitates heightened awareness and proactive measures for management. By understanding the symptoms, recognizing their connection, and implementing a heart-healthy diet alongside regular testing, individuals can take charge of their health. Remember, early detection and lifestyle changes are key to preventing complications associated with both conditions.
Taking care of your heart while managing diabetes is not just important for your overall health but also essential for a long, fulfilling life. Empower yourself with knowledge, commit to a healthier lifestyle, and reach out for support when needed. Your health is worth it!



