Diabetes Types: Type 1, Type 2, Gestational, and More
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Its impact is profound, affecting not only the lives of those diagnosed but also their families, communities, and healthcare systems. Awareness and education about diabetes, particularly Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational diabetes, are crucial for early detection, prevention, and management. This article aims to shed light on these three types of diabetes, their causes, symptoms, complications, and the importance of proactive management. Join us in raising awareness and taking action for a healthier future!
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, resulting from the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use it effectively. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational diabetes.
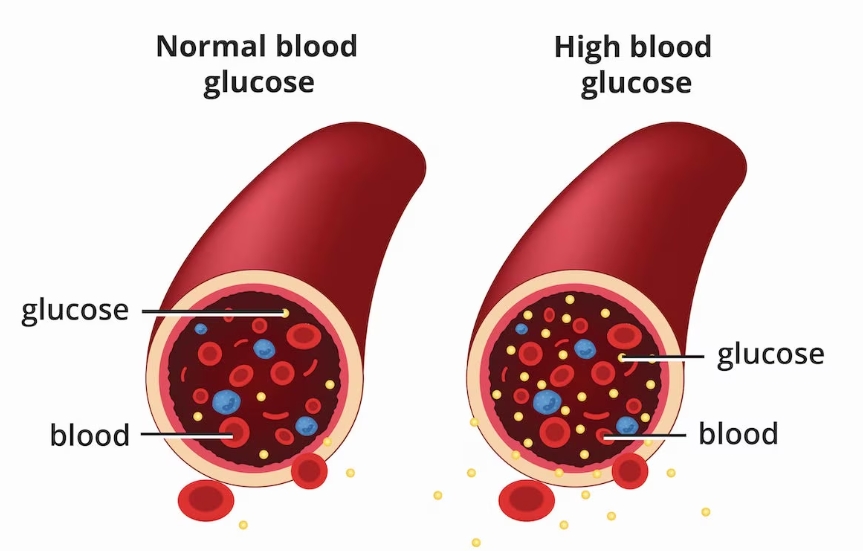
Type 1 Diabetes
Overview
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This leads to an absolute insulin deficiency, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
Causes
While the exact cause of Type 1 diabetes remains unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, such as viral infections.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Extreme hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically done through fasting blood sugar tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, and HbA1c tests. A confirmed diagnosis is essential for initiating proper management.

Treatment and Management
Managing Type 1 diabetes requires a multifaceted approach:
- Insulin Therapy: Individuals need lifelong insulin therapy, which can be administered via injections or an insulin pump.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels is critical for effective management. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can provide real-time data.
- Diet and Exercise: Adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise can help control blood sugar levels. Carbohydrate counting is a useful tool for meal planning.
- Education: Knowledge about diabetes is empowering. Education about managing blood sugar, recognizing symptoms, and handling emergencies is vital for individuals with Type 1 diabetes and their families.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Living with Type 1 diabetes can be challenging, but it doesn’t mean individuals can’t lead fulfilling lives. Support groups, counseling, and resources are available to share experiences and coping strategies.

Type 2 Diabetes
Overview
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all diabetes cases. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity and overweight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of diabetes
- Poor diet high in refined sugars and processed foods
- Age, particularly after 45
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds
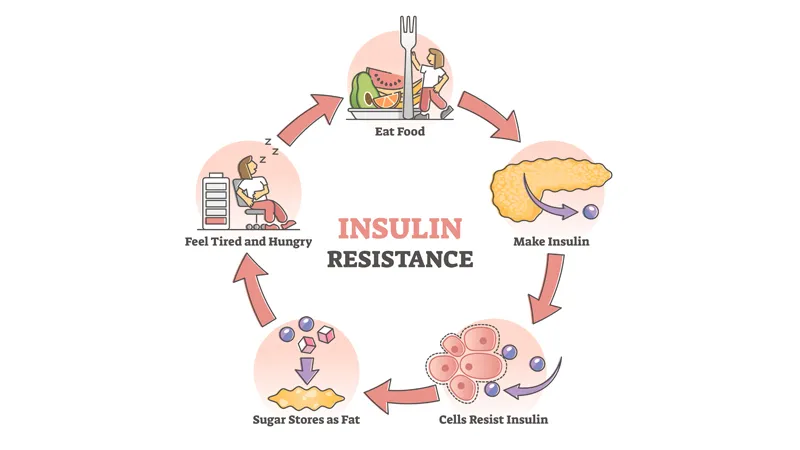
Diagnosis
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed similarly to Type 1 diabetes, through blood tests assessing blood sugar levels.
Treatment and Management
Preventing and managing Type 2 diabetes involves lifestyle modifications:
- Dietary Changes: A balanced, nutrient-rich diet can help manage blood sugar levels. Incorporating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential.
- Regular Physical Activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly can reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and improve overall health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce insulin resistance. Even a modest weight loss can have a positive impact.
- Medications: In some cases, oral diabetes medications or insulin may be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels.
The Importance of Regular Screenings
Regular screening for Type 2 diabetes is essential, particularly for individuals at higher risk, such as those with a family history of diabetes, obesity, or hypertension. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management, reducing the risk of complications.
Living with Type 2 Diabetes
Living with Type 2 diabetes requires ongoing management and self-monitoring. Education about the condition empowers individuals to make informed choices regarding their health.

Gestational Diabetes
Overview
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet increased demands. It affects about 2-10% of pregnancies and usually resolves after childbirth, but it poses risks for both the mother and baby.
Causes
The exact cause of gestational diabetes is not fully understood, but risk factors include:
- Obesity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age over 25
- Ethnicity, with higher rates in certain populations
Symptoms
Gestational diabetes may not present noticeable symptoms but can be diagnosed through routine screening tests during pregnancy. Symptoms may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Diagnosis
Pregnant women typically undergo a glucose tolerance test between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation to check for gestational diabetes.

Treatment and Management
Management of gestational diabetes involves:
- Dietary Changes: A well-balanced diet focused on whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential.
- Physical Activity: Moderate exercise can help regulate blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar: Regular blood sugar monitoring helps ensure that levels remain within a target range.
- Medications: If lifestyle changes are insufficient, insulin therapy may be necessary.
Implications for Mother and Baby
Gestational diabetes increases the risk of complications during pregnancy, including high birth weight and preterm birth. Mothers are also at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Postpartum Considerations
Post-delivery, women should have their blood sugar levels checked, as gestational diabetes increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Regular screenings and lifestyle adjustments are crucial for long-term health.
The Importance of Awareness and Education
Understanding diabetes, its types, causes, symptoms, complications, and management options is vital for effective prevention and treatment. Public awareness campaigns play a critical role in disseminating information and encouraging healthy lifestyle choices.
Advocacy and Support
Advocacy groups and healthcare organizations are dedicated to raising awareness and supporting individuals affected by diabetes. They provide resources, education, and community support for those living with diabetes and their families.
Call to Action
Diabetes is not just a personal health issue; it’s a public health concern that requires collective action. By educating ourselves and others, we can work towards prevention, early detection, and effective management of diabetes.
- Get Informed: Learn about diabetes and its risk factors.
- Raise Awareness: Share knowledge with friends, family, and your community.
- Screen Regularly: Encourage regular screenings for early detection.
- Support Those Affected: Join local support groups and advocacy efforts.
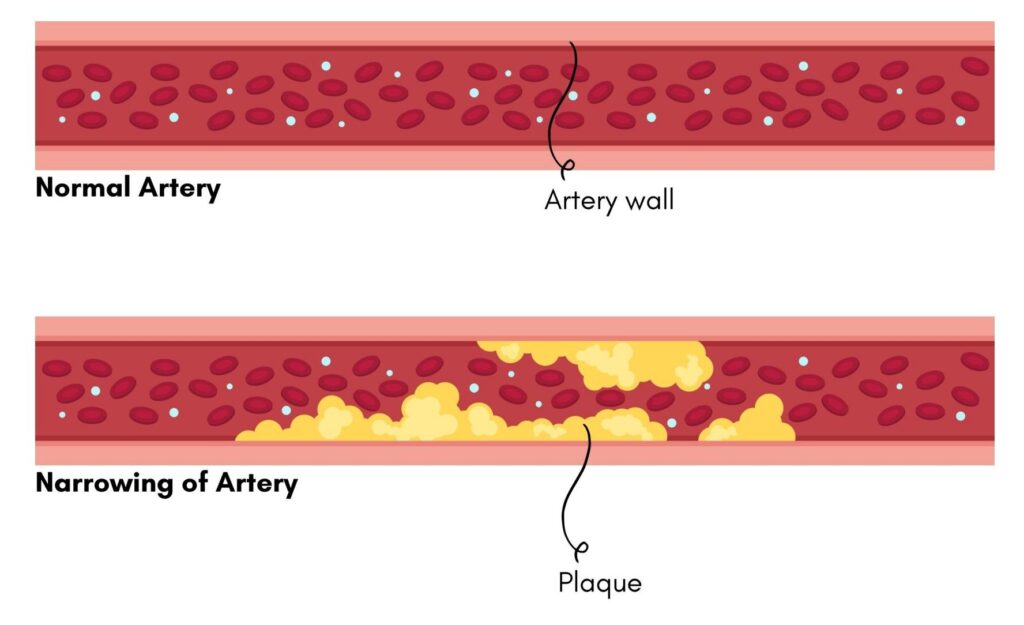
Diabetes, whether Type 1, Type 2, or Gestational, is a condition that affects individuals across different demographics. With proactive management, education, and a supportive community, we can improve outcomes for those living with diabetes. Let’s unite to raise awareness and promote a healthier future for everyone. Your actions today can pave the way for a brighter tomorrow—take the first step towards understanding and managing diabetes. Together, we can make a difference!



